What is UI?
A UI, which means User Interface, is anything a user can or will interact with to use an application (or it can be a product or a service). This includes everything from smartwatch screens to the home theater screen. Simply, a user interface or human-machine interface is a part of the machine that handles human-machine interaction. Now, you might wonder why I mention the phrase human-machine interface. That’s because humans and machines see the world differently. So, they cannot communicate because the machines use and understand only the machine language. But it is tough for humans to understand machine language. It would be easy for them to understand the natural languages. That is the moment where the UI interferes.
UI helps humans to interact with machines because the UI makes it easy, efficient, and enjoyable (or user-friendly) to operate a machine in a way that produces the needed results (maximum usability). So, knowing only what UI is not going to help us. So, when we come to the next question, “What is UI (User Interface) Design?”
What is User Interface Design?
User Interface Design is the process or approach designers use to build interfaces in software or computer-based devices, focusing on looks or style. Mainly we use wireframes and UI designs to select the best UI design that fits the application.
Eight qualities of great UI
According to Wikipedia, eight qualities and characteristics are shared by all the great interfaces we can see in the modern world.
- Clarity: The interface avoids ambiguity by making everything clear through language, flow, hierarchy, and metaphors for visual elements.
- Concision: It’s easy to make the interface clear by over-clarifying and labeling everything. However, this leads to interface bloat, where there is just too much stuff on the screen simultaneously. If too many things are on the screen, finding what we need is difficult. So, the real challenge in making a neat interface is simultaneously making it concise and clear.
- Familiarity: Some elements can still be familiar when someone uses an interface for the first time. Natural life metaphors can be used to communicate meaning.
- Responsiveness: A good interface should not feel inactive. This means that the interface should provide good feedback to the user about what’s happening and whether the user’s input is being successfully processed.
- Consistency: Keeping your interface consistent across your application is crucial because it allows users to recognize usage patterns.
- Aesthetics: While you don’t need to make an interface attractive for it to do its job, making something look good will make the time your users spend using your application more enjoyable, and happier users can only be a good thing.
- Efficiency: Time is money, and an excellent interface should make the user more productive through shortcuts and good design.
- Forgiveness: A good interface should not punish users for their mistakes but instead provide the means to remedy them.
What is UX?
UX or, User Experience is something that evolved as a result of the improvements to UI.
The above definition says that the user experience is more important. Because it doesn’t matter whether the UI or the interface design is more attractive or beautiful, the design uses various colors; if the UX fails, it means the whole interface fails. Because the UX or the user experience is a thing that users have used for a long time, if you want a better interface, you can develop the UX, but it should be better than the previous, what the users are used to.
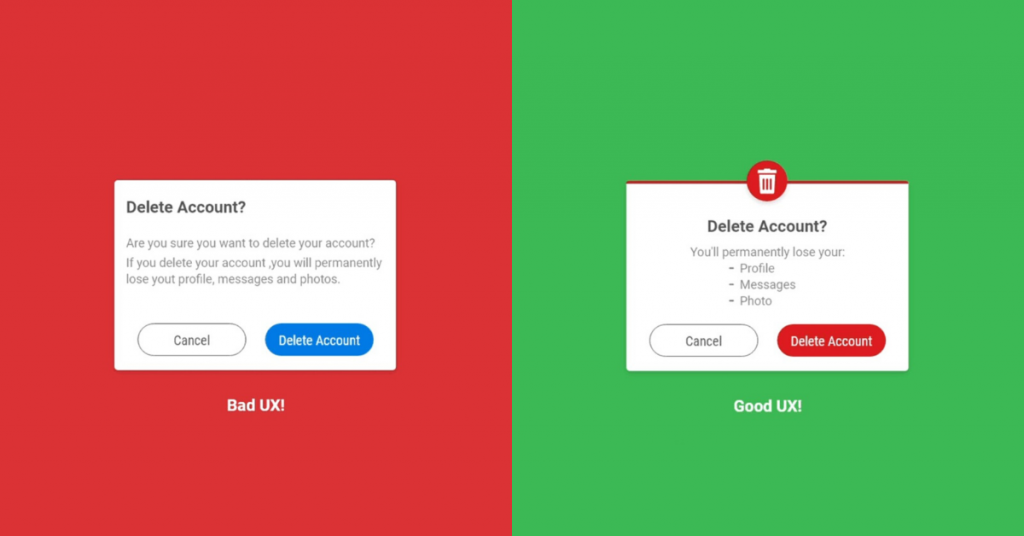
Both interfaces are good UI designs, but the one on the left is a failure when we come to the UX part. It is terrible. But the right one is good. Why is that? What is the difference? That is because of their color combination, the text format, and the red delete button. See, when you get
the left interface without saying anything, you will say, “it’s nice.” And if you got the right one, you also say, “it’s nice,” but more than that, you feel that you are on a delete account page, aren’t you? That is the difference between bad and good UX.
What’s the Different Between UI & UX ?
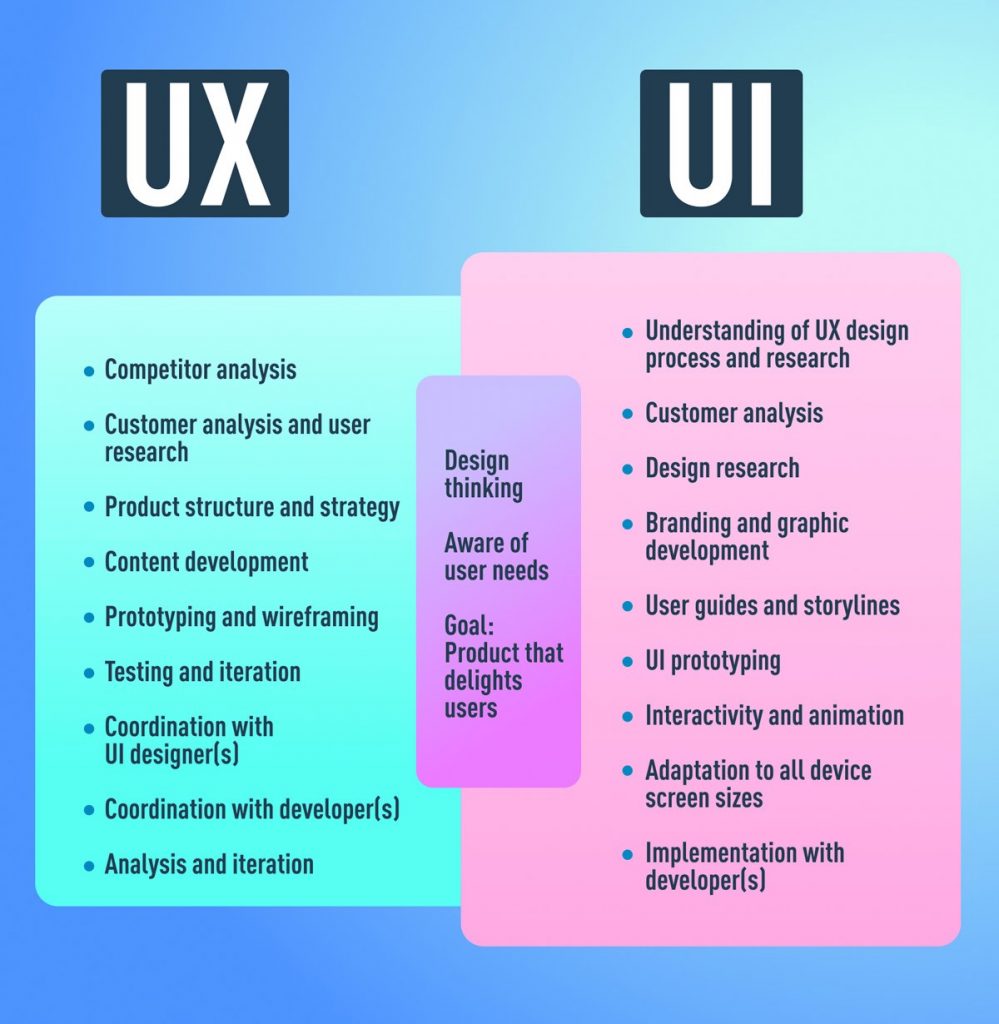
Are you still confused? Don’t worry. You are not the only one. Okay, think about that like this: think about the human body. The bones represent the code that gives the human body its structure. The organs represent the UX design of the body: measuring and optimizing against input for supporting life functions. See, there are no organs placed in the wrong places because the organs are placed inside the body at the correct locations to make it easy to work. And finally, the UI design represents the cosmetics of the body, its presentation, its senses, and reactions.
The UX design is all about the overall feel of the experience, while the UI design is about how the product’s interface looks and functions.
5 Principles of visual design in UX
When doing some research, I found five visual-design principles that impact UX:
- Scale
- Visual hierarchy
- Balance
- Contrast
- Gestalt
Scale
The scale principle refers to using relative size to signal importance and rank in a composition.
Visual Hierarchy
The principle of visual hierarchy refers to guiding the eye on the page to attend to design elements in order of importance.
Balance
Balance occurs when an equally distributed amount of visual signal is on both sides of an imaginary axis.
Contrast
The principle of contrast refers to juxtaposing visually different elements to convey that their elements are different.
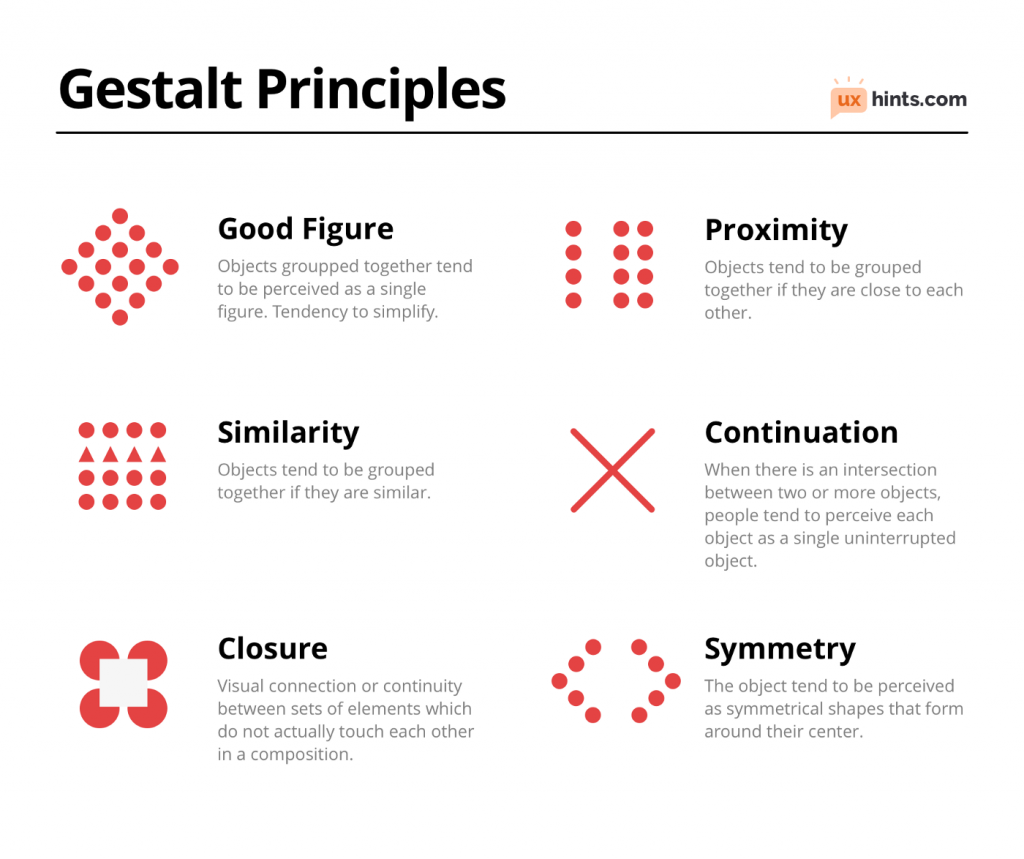
Gestalt
Gestalt principles capture our tendency to perceive the whole instead of the individual elements.